Safety Policy, HSE Policy, and IMS Policy:
3 Essential Workplace Policies
You Must Know
Learn about the 3 essential workplace policies—Safety Policy, HSE Policy, and IMS Policy—that protect employees, ensure compliance, and boost operational efficiency.

These three essential workplace policies Safety Policy, HSE Policy, and IMS Policy are vital for every organization. They protect employees by reducing workplace risks and promoting a safe environment. They ensure compliance with legal, regulatory, and international standards. By streamlining processes, they enhance operational efficiency and productivity. Understanding these policies helps organizations build a strong safety culture and achieve continuous improvement.
1. Safety Policy
Definition:
Safety policy is an organization’s formal commitment to protecting workers from accidents and injuries. Its focus is on creating a safe workplace by controlling risks and unsafe practices. The policy defines the responsibilities of management and employees to ensure safety. Its core aim is to prevent harm and promote a culture of protection at work.
Purpose and Importance:
The safety policy is the foundation of any workplace safety system. It communicates the organization’s commitment to safeguarding its employees and establishes clear expectations for safe behavior. Key aspects of a safety policy include:
-
Risk Management: Identifying potential hazards in the workplace and implementing control measures to minimize risks.
-
Responsibility Assignment: Clearly defining the roles of management, supervisors, and workers in maintaining safety standards.
-
Accident Prevention: Establishing procedures to prevent incidents and reduce workplace injuries.
-
Safety Culture Promotion: Encouraging employees to adopt safe practices as part of everyday operations.
Practical Example:
In a construction company, a safety policy may mandate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, gloves, and safety harnesses. Supervisors are responsible for ensuring compliance, while employees are accountable for following safety guidelines. This shared responsibility helps reduce accidents and promotes a proactive safety culture.
2. HSE Policy
Definition:
HSE policy is broader and more comprehensive than a safety policy. It covers health, safety, and environment together in one framework. HSE policy ensures the well-being of employees, accident prevention, and environmental protection. The policy highlights legal compliance, training, and continuous improvement. Its goal is sustainable operations where people and nature remain safe.
Purpose and Importance:
Unlike a standard safety policy that focuses mainly on preventing workplace accidents, an HSE policy integrates health and environmental considerations. This approach benefits organizations by promoting holistic safety and sustainability. Key components include:
-
Employee Well-being: Ensuring workers are protected not only from physical hazards but also from occupational health risks.
-
Environmental Protection: Implementing measures to minimize the organization’s impact on the environment, such as waste management, emission control, and resource conservation.
-
Legal Compliance: Ensuring adherence to local, national, and international laws and regulations concerning workplace safety, health, and environmental protection.
-
Training and Awareness: Providing employees with the knowledge and skills to work safely and responsibly.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing policies and procedures to enhance safety, health, and environmental performance.
Practical Example:
In an oil and gas company, an HSE policy may require routine health check-ups for workers, strict handling procedures for hazardous chemicals, and environmental audits to prevent pollution. Employees are trained to respond to emergencies, and the organization continuously updates its practices to align with legal requirements and industry standards.
3. IMS Policy
Definition:
Integrated Management System (IMS) policy unites quality, health & safety, and environmental standards in a single framework. It improves efficiency by reducing duplication of processes and resources. IMS ensures compliance with international standards and legal requirements. The main goal of IMS is continuous improvement and sustainable performance.
Purpose and Importance:
IMS policy is designed for organizations that aim to streamline management systems and achieve operational excellence. By integrating multiple ISO standards such as ISO 9001 for quality, ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety, and ISO 14001 for environmental management—IMS helps organizations optimize resources and maintain compliance. Key benefits include:
-
Operational Efficiency: Reduces duplication of processes and minimizes administrative workload.
-
Unified Framework: Combines quality, safety, and environmental requirements into a single system.
-
Compliance Assurance: Ensures adherence to national and international standards and legal obligations.
-
Continuous Improvement: Promotes ongoing evaluation and enhancement of processes, products, and services.
-
Sustainable Performance: Aligns organizational goals with long-term safety, quality, and environmental objectives.

Practical Example:
A manufacturing plant implementing IMS may integrate quality audits, safety inspections, and environmental monitoring into one cohesive system. This allows management to identify overlapping risks, improve efficiency, and ensure the organization meets customer expectations, legal requirements, and sustainability goals simultaneously.
Basic Difference Between Safety, HSE and IMS Policies:
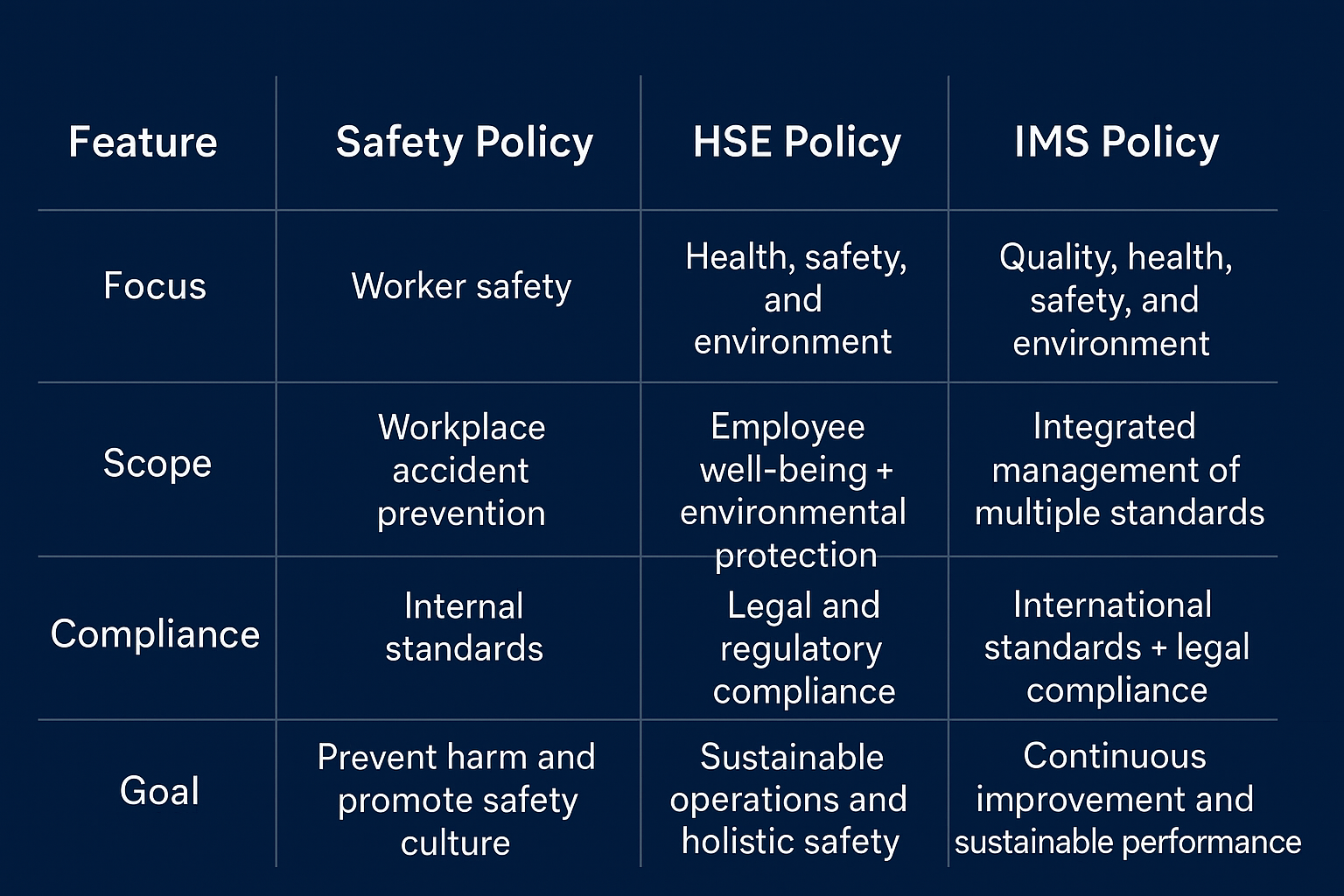
Conclusion:
Safety Policy, HSE Policy, and IMS Policy form the backbone of a secure, compliant, and efficient workplace. While the safety policy focuses on accident prevention, HSE policy ensures employee well-being and environmental protection, and IMS policy integrates quality, safety, and environmental standards for continuous improvement. Understanding and implementing these policies empowers organizations to foster a strong safety culture, reduce risks, and enhance overall operational performance.
CTA:
Stay updated on workplace safety and management policies! Follow us on Facebook, for expert insights, tips, and latest updates in health, safety, and management systems.
FAQs:
-
What is the main purpose of a Safety Policy?
To prevent workplace accidents, define responsibilities, and promote a safe work environment. -
How does an HSE Policy differ from a Safety Policy?
HSE policy includes health and environmental considerations along with safety, offering a holistic approach to workplace well-being. -
What is IMS Policy in simple terms?
IMS policy integrates quality, safety, and environmental management into a single system to improve efficiency and ensure compliance. -
Why are these policies important for employees?
They protect employees from risks, ensure legal compliance, and create a culture of safety and accountability. -
Can small organizations benefit from IMS?
Yes, IMS helps small and large organizations streamline processes, reduce duplication, and achieve sustainable growth.
